中图分类号: R730.7 G35
通讯作者:
收稿日期: 2016-10-31
修回日期: 2016-12-5
网络出版日期: 2017-02-25
版权声明: 2017 《数据分析与知识发现》编辑部 《数据分析与知识发现》编辑部
基金资助:
展开
摘要
【目的】利用SEER数据库, 找出对非小细胞肺癌患者预后生存的影响因素并预测患者预后生存状态, 指导肿瘤预后评价。【方法】采用单因素统计学方法及Logistic回归分析初步筛选预后相关因素, 利用贝叶斯网络方法构建患者术后生存预测模型, 并与其他三种常见的机器学习分类算法所建模型效能做比较。【结果】最终纳入模型的预后变量共5项, 包括年龄、肿瘤大小、组织学分级、肿瘤分期和受累淋巴结比率。贝叶斯网络所建模型对非小细胞肺癌患者生存状况预测准确率达到72.87%。【局限】SEER数据库内纳入的预后因素有限, 一定程度影响预测效果。【结论】贝叶斯网络可探寻变量间的关系并构建肺癌患者最优预后模型, 辅助医生判断患者预后情况及治疗效果, 优于决策树、支持向量机及人工神经网络三种模式。
关键词:
Abstract
[Objective] This study aims to improve the tumor-prognostic assessment for Asian patients who were diagnosed with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). The proposed model identifies the influencing factors of the patients’ survival status and predicts their prognostic situation. [Methods] First, we used single factor statistical method and logistic regression to identify the prognostic variables. Second, we employed the Bayesian Network algorithm to construct the prognostic survival model for the Asian NSCLC patients. Finally, we compared the performance of our model with three other algorithms. [Results] The identified prognostic variables include age, tumor size, grade, tumor stage, as well as the lymph nodes ratio. The proposed model could predict NSCLC patients’ prognostic survival status effectively. [Limitations] The SEER database had limited number of prognostic factors, which may influence the prediction accuracy. [Conclusions] The Bayesian Network could help us build optimal prognosis model for cancer patients to improve their survival rates. The proposed model is better than the Decision Tree, Support Vector Machine and Artificial Neural Network models.
Keywords:
肺癌是肿瘤患者死亡的主要原因, 其中非小细胞肺癌(Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, NSCLC)约占所有肺癌病例的83%, 其发病率为40.60/10万, 5年生存率仅为22.1%[1]。非小细胞肺癌发病率高且预后差, 对其预后的判断就尤为重要。目前临床医生通常根据手术病理分期判断预后, 但该分期仅考虑到肿瘤原发灶、区域淋巴结受累和远处转移三方面, 忽略了其他预后影响因素的作用, 预测效果差[2]。目前少有的预后研究多以单独或较少几个医疗机构为主要研究单位, 随访数据缺失多、数据量小、可信度差。临床上亟需有基于较大量数据、可信度高、预测效果好的非小细胞肺癌患者预后预测评估体系。
美国国家癌症研究所(National Cancer Institute, NCI)于1973年建立了监测、流行病学及预后数据库(Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results, SEER), 是世界公认的肿瘤患者随访数据权威来源之一, 为临床研究提供了可靠的数据支持, 有学者利用此数据库, 采用简单统计学方法建立了横纹肌肉瘤等疾病生存预测模型。本研究将利用SEER数据库, 提取其中的亚洲人NSCLC病例, 采用更能反映预后变量之间相关关系且适用性更好的机器学习方法, 构建亚洲人NSCLC预后模型及预测评估体系, 为临床医生开展治疗与判断预后提供决策支持。
国内外对疾病预测模型的研究已经有一定基础。Muers等[3]获取6所医疗机构中NSCLC患者数据建立其预后风险模型, 并将模型所输出的生存期与临床医生的判断作比较; Yang等[4]基于SEER数据库构建横纹肌肉瘤患者5年及10年生存预测模型以指导治疗方法的选择; Park等[5]利用临床试验数据, 预测采用姑息化疗的晚期胆道腺癌患者的生存情况。以上模型均先筛选预后因素再采用统计学中的COX回归方法构建模型, 这也是构建医学预测模型的常见方法。但COX回归分析难以看出预后变量之间的关系, 为提高模型的适用性, 机器学习方法逐渐受到研究者的推崇。如Kim等[6]应用朴素贝叶斯方法并绘制诺模图(Nomogram), 通过7项指标得到术后复发的可能性, 该研究者曾于2012年使用支持向量机方法预测乳腺癌患者术后5年生存情况[7], 而后构建在线预后系统。
自21世纪初开始, 国内越来越多的研究者开始从机器学习方向出发评价肿瘤及其他疾病的发生、发展和预后。刘雅琴[8]基于SEER数据库使用Logistic回归、人工神经网络、决策树三种方法比较预后预测模型效果, 是国内此领域研究肿瘤预后的重要突破。台湾学者Chen等[9]使用人工神经网络对4个医疗机构的NSCLC患者的临床及基因表达数据进行探究, 建立生存状况风险模型; 牟冬梅等[10]通过提取电子病历信息进而构建妊娠高血压综合征危险因素预测模型, 得到决策树模型为最优。但是以上研究的变量纳入均凭借已有经验, 缺少与临床医生的交流, 未实现跨学科的合作。
通过文献研究发现: 肿瘤中发病率及死亡率均较高的肺癌的预后研究屈指可数。因此, 本文基于SEER数据库, 确定患者预后因素并参考肿瘤医生的意见进行调试, 利用更能反映预后变量之间相关关系且适用性更好的机器学习方法, 以提升预测准确率为目标, 构建亚洲NSCLC患者术后生存模型, 更好地为临床预后评价服务。
肿瘤的预后包括风险评估、复发、转移及生存情况评价[11]。以NSCLC患者术后5年为时间基准, 对患者的生存情况即“生存”与“死亡”进行预测, 具体研究流程如图1所示。
具体步骤如下:
(1) 数据下载: 在SEER*Stat软件中调用Incidence-SEER18 Regs Research Data+Hurricane Katrina Impacted Louisiana Cases, Nov2014版本数据, 该版本数据随访终止日期为2012年年末, 并根据ICD-O-3恶性肿瘤形态学编码, 下载NSCLC患者数据。
(2) 变量选取依据: 参考美国癌症联合会(American Joint Committee on Cancer,AJCC)、美国国立癌症网络(The National Comprehensive Cancer Network, NCCN)临床指南及美国第二版肿瘤信息采集系统[12-13] (Collaborative Stage Manual Online Help, CS)中所提及与患者生存相关的预后因素, 并从SEER*Stat中提取含有上述变量的所有字段, 以首次确诊时所登记的患者信息为准, 将整理后的患者数据录入Excel表。
(3) 特征变量筛选: 为确定各变量是否独立影响患者的生存情况, 首先应用SPSS22.0软件对训练样本进行单因素分析(独立样本t检验或卡方检验), 而后将经单因素分析得到的变量纳入Logistic回归分析, 并筛选NSCLC高相关预后因素, P<0.05具有统计学意义, 结合临床医生的建议调整变量纳入最终模型。
(4) 肿瘤预后模型的构建: 选用机器学习中的监督学习方法, 进行肿瘤预后预测模型的构建[10]。应用R Studio软件建立贝叶斯生存预测模型, 并完成贝叶斯网络的结构调整, 构建有效的预后模型。
(5) 模型评价: 选用数据挖掘软件WEKA比较贝叶斯网络模型及其他三种常见分类模型的预测准确性、精确度及ROC曲线下面积。
(1) 研究对象
选取自2004年起被确诊为NSCLC的亚裔患者为最终研究对象, 其中包含5年内直接因NSCLC致死和随访期满5年且仍然生存的患者, 共计683位。
(2) 研究变量
在SEER中提取17项预后研究变量: 性别、国别、婚姻状况、发病部位、病理类型、组织学分级、患侧部位、邻近器官浸润程度、区域淋巴结累积程度、远处转移程度、肿瘤分期、手术类型、是否接受放疗以及确诊时年龄、肿瘤大小、阳性淋巴结数量及受检淋巴结数量, 其中后4项指标为连续型变量, 其余均为分类变量, 如表1所示。
表1 非小细胞肺癌患者预后指标信息
| 数据类型 | 变量 | SEER中所示名称 | 类数/数值范围 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 分类型 | 性别 | Sex | 2 |
| 国别 | Race recode (Asian) | 8 | |
| 婚姻状况 | Marital status at diagnosis | 4 | |
| 发病部位 | Primary Site - labeled | 5 | |
| 病理类型 | ICD-O-3 Hist/behav, malignant | 4 | |
| 组织学分级 | Grade | 4 | |
| 患侧部位 | Laterality | 2 | |
| 邻近器官 浸润程度 | CS extension | 18 | |
| 区域淋巴结 累积程度 | CS lymph nodes | 5 | |
| 远处转移程度 | CS mets at dx | 5 | |
| 肿瘤分期 | Derived AJCC Stage Group | 7 | |
| 手术类型 | RX Summ--Surg Prim Site | 13 | |
| 是否放疗 | Radiation | 3 | |
| 连续型 | 确诊时年龄 | Age at diagnosis | 26-90 |
| 肿瘤大小 | CS tumor size | 4-132 | |
| 阳性淋巴结数量 | Regional nodes positive | 0-23 | |
| 受检淋巴结数量 | Regional nodes examined | 1-45 |
(3) 结局变量
肿瘤患者5年生存情况是评价预后效果的重要指标。以NSCLC患者术后5年的生存情况作为应变量。其中生存期以月为单位, 对其进行分类变量的转换, 即生存时间在60个月及以上的患者被视为“生存”(记为1), 否则即为“死亡”(记为0)。
(4) 特征变量选择
为减少预后变量, 提高模型的预测准确性, 需对纳入研究变量进行高相关预后因素选择。经单因素分析后初步纳入的变量有(P<0.05): 确诊时年龄、肿瘤大小、组织学分级、肿瘤分期、邻近器官浸润程度、区域淋巴结累积程度、阳性淋巴结数量、婚姻状况、国别、远处转移程度、手术类型及是否放疗。在单因素分析的基础上经Logistic回归分析筛选出的预后变量有(P<0.05): 确诊时年龄、肿瘤大小、组织学分级、肿瘤分期、受检淋巴结数量及阳性淋巴结数量。筛选结果如表2所示。
表2 Logistic回归分析筛选变量结果
| 变量名称 | B | S.E. | Exp(B) | 95% Exp(B) | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||
| 确诊时年龄 | -0.066 | 0.011 | 0.936 | 0.916 | 0.957 | 0.000 |
| 肿瘤大小 | -0.018 | 0.007 | 0.982 | 0.968 | 0.996 | 0.014 |
| 组织学分级 | / | / | / | / | / | 0.001 |
| 肿瘤分期 | / | / | / | / | / | 0.013 |
| 受检淋巴结 数量 | 0.050 | 0.017 | 1.051 | 1.016 | 1.087 | 0.004 |
| 阳性淋巴结 数量 | -0.199 | 0.067 | 0.819 | 0.719 | 0.934 | 0.003 |
受累淋巴比率(Lymph Nodes Ratio, LNR)为阳性淋巴结数量与受检淋巴结数量的比值, 参考临床医生的意见, 将LNR代替阳性淋巴结数量和受检淋巴结数量两项作为预后变量, 即最终进入模型的变量为: 确诊时年龄、肿瘤大小、组织学分级、肿瘤分期及受累淋巴比率。
(5) 数据预处理
删除数据缺失严重、记录错误及因非肺癌致死的患者信息, 选用Interval方法对数值型数据进行离散化。该离散化方法旨在将区间 [X0,XN-1]划分为同样大小的子区间D并根据所属子区间指数给出离散化意见, 其中观察指数i与离散水平j满足以下条件[14]:
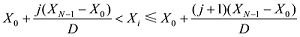
在软件R Studio中调用bnlearn的函数包实现以上数据预处理步骤。而后按照约70%与30%的比例[15]将数据分为训练集(N1=495)和测试集(N2=188), 训练集用来进行网络学习及调整, 从而构建预后模型, 测试集则用来评价模型的性能。
(6) 预后模型的构建及预测结果
贝叶斯网络(Bayesian Network, BN)通过表示变量的节点和表示变量间关系的连线描述子节点与父节点间的依赖关系[16], 已知随机变量X = {X1, X2, …, Xn}, 其联合概率分布为:
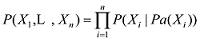
其中, Pa(Xi)是Xi父节点的子集, 在网络图中Xi独立于其非直系节点变量。选用禁忌搜索(Tabu Search, TS)方法对贝叶斯网络进行初步学习。该方法于1986年由美国工程学院院士Fred Glover提出[17], 是一种基于邻域和迭代来求解优化问题的启发式算法。该方法的本质是禁止重复前面的工作, 跳出局部搜索最优点, 即在区域中随机移动并产生新的方案, 而后将评估每一个相邻的解决方案, 并选择最能提高目标函数的路径, 若没有能提高最终结果的方案, 则选取对目标函数影响最小的方案, 通过模仿人类记忆找出最佳结果[18], 步骤如下:
①确定区域N(x), 从中选定一个初始可行解X0, 使当前最优解Xbest=X0, 则T=N(Xbest);
②按照上述步骤依次组合, 并得到最新解 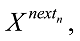
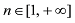
③比较所有决策结果并输出全局决策最优解 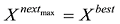
Makond等[19]所构建的贝叶斯预后模型并未完全根据所得数据进行学习, 而是通过听取医生意见建立患者预后生存模型, 实际上是基于实际经验的建模思维。本研究克服单以实际经验建模的弊端, 结合网络学习方法TS与医生意见共同建立患者预后模型, 在R Studio软件中实现网络模型的修整与优化, 最终的网络模型如图2所示。
在R Studio软件中使用caret包输出预测样本及实例所组成的表格及预测模型评价指标。本研究共188个测试集样本, 预测正确137例, 预测正确率达72.87%。
另选用决策树、支持向量机及人工神经网络方法建立预后模型, 并根据预测结果与本研究所构建的预后模型作对比。在WEKA中分别选择三种方法所对应的J48、SMO及Multilayer Perceptron建立预后模型, 参数默认。4种机器学习算法建模的预测准确性及模型性能评价比较如表4-表5所示。
表4 BNNSCLC模型与其他三种分类算法所建模型预测准确率比较
| 所用分类算法 | 预测准确率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 测试集 | |
| 贝叶斯网络 | 0.683 | 0.729 |
| 决策树 | 0.713 | 0.670 |
| 支持向量机 | 0.733 | 0.686 |
| 人工神经网络 | 0.784 | 0.649 |
表5 不同算法所构建模型性能比较
| 算法 | 预测准确率 | 精确度 | ROC曲线下面积 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 贝叶斯网络 | 72.87% | 71.0% | 0.67 |
| 决策树 | 67.02% | 66.3% | 0.568 |
| 支持向量机 | 68.62% | 68.2% | 0.611 |
| 人工神经网络 | 64.89% | 63.7% | 0.615 |
本研究发现贝叶斯网络所构建的NSCLC预后模型最优。由表4可知, 虽然决策树、支持向量机及人工神经网络在训练集上的预测准确性均高于贝叶斯网络, 但在测试集中三者预测准确性的数值与训练集相比显著下降, 未能很好地适应新数据, 不适于实际应用, 模型的拟合程度不如贝叶斯网络模型。另通过对表5的解读, 贝叶斯网络模型在预测准确率、精确度及ROC曲线下面积的数值均高于其他三种机器学习算法。
网络学习方法的选择是构建贝叶斯分类器的基础。本研究选用TS方法初步对网络模型进行构建, 是对爬山法的优化, 当已知构成某网络变量并不产生网络环路的基础上, 以移动搜索代替随机产生, 采用加、减及逆向边三种操作产生邻域[20], 并搜索全局最优解来调整网络结构以完成贝叶斯网络的自学习。在此基础上, 结合临床医生的经验修改网络图, 将高相关预后因素相联系, 是理论方法与实际应用的典型结合。
网络图的调整是该生存预测模型构建研究的最关键流程。如图2所示, 箭头方向表示节点间的关系, 如size指向stage即为前者直接对后者产生影响, 所选预后变量均指向最终变量生存状态, 其中确诊时年龄、肿瘤分期及受累淋巴比率直接影响患者的生存情况。通过构建不同的网络图找到最优分类模型, 从而判断各预后因素间的关系及对生存状态的影响, 临床可据此评价肿瘤患者术后的预后情况, 并对相关因素进行控制。当然, 由于本研究所采用的SEER数据库并未将所有肿瘤预后因素全部纳入库中[21], 故建模所选指标的数量有限, 该预测模型可能存在一定局限性。
本研究以非小细胞肺癌患者术后生存状态为目标构建患者生存预后模型, 预测准确率达72.87%。通过构建贝叶斯网络探寻预后变量间的关系及对患者生存情况的影响, 在网络结构内部调整的基础上结合临床专家的建议, 更好地诠释了模型中节点间关系。首次应用SEER数据库, 以亚洲肿瘤患者为主要研究对象构建其生存预测模型, 对判断患者术后5年的预后情况起到辅助作用, 具有应用前景。在未来的研究中, 可考虑其他来源患者外部验证的纳入, 提升预测模型自身的适应程度, 更好地为临床治疗及预后评价服务。
尹玢璨: 设计研究方案, 数据分析, 构建模型, 撰写论文;
辛世超: 数据预处理, 建模实验;
张晗: 修改论文;
赵玉虹: 提出研究思路, 论文最终版本修订。
所有作者声明不存在利益冲突关系。
支撑数据由作者自存储, E-mail: yinbincan0803@163.com。
[1] 尹玢璨. NSCLC.csv. 亚洲非小细胞肺癌患者预后模型研究原始数据.
[2] 尹玢璨. data.csv. 亚洲非小细胞肺癌患者建模数据.
| [1] |
SEER Cancer Statistics Review (CSR) 1975-2013 [R/OL]. [ |
| [2] |
NCCN Guidelines Insights: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 4.2016 [J].URL PMID: 26957612 [本文引用: 1] 摘要
These NCCN Guidelines Insights focus on recent updates in the 2016 NCCN Guidelines for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC; Versions 1-4). These NCCN Guidelines Insights will discuss new immunotherapeutic agents, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, for patients with metastatic NSCLC. For the 2016 update, the NCCN panel recommends immune checkpoint inhibitors as preferred agents (in the absence of contraindications) for second-line and beyond (subsequent) therapy in patients with metastatic NSCLC (both squamous and nonsquamous histologies). Nivolumab and pembrolizumab are preferred based on improved overall survival rates, higher response rates, longer duration of response, and fewer adverse events when compared with docetaxel therapy.
|
| [3] |
Prognosis in Lung Cancer: Physicians’ Opinions Compared with Outcome and a Predictive Model [J].https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.51.9.894 URL PMID: 8984699 [本文引用: 1] 摘要
BACKGROUND: Although the study of prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer has reached the stage where they are used to guide treatment, fewer data are available for non-small cell lung cancer. Although correct management decisions in non-small cell lung cancer depend upon a prognostic assessment by the supervising doctor, there has never been any measurement of the accuracy of physicians' assessments. METHODS: A group of consecutive patients with non-small cell lung cancer was studied and the predictions of their physicians as to how long they would survive (in months) was compared with their actual survival. A prognostic index was also developed using features recorded at the patients' initial presentation. RESULTS: Two hundred and seven consecutive patients diagnosed and managed as non-small cell lung cancer, who did not receive curative treatment for their condition, were studied. Of the 196 patients whose date of death was known, physicians correctly predicted, to within one month, the survival of only 19 patients (10%). However, almost 59% of patients (115/196) had their survival predicted to within three months and 71% (139/196) to within four months of their actual survival. Using Cox's regression model, the sex of the patient, the activity score, the presence of malaise, hoarseness and distant metastases at presentation, and lymphocyte count, serum albumin, sodium and alkaline phosphatase levels were all identified as useful prognostic factors. Three groups of patients, distinct in terms of their survival, were identified by the use of these items. When the prediction of survival made by the physician was included as a prognostic factor in the original model, it was shown to differentiate further between the group with a poor prognosis and the other two groups in terms of survival. CONCLUSIONS: Physicians were highly specific in identifying patients who would live less than three months. However, they had a tendency to overestimate survival in these patients, failing to identify almost half the patients who actually died within this time. Both the physicians and the prognostic factor model gave similar performances in that they were more successful in identifying patients who had a short time to survive than those who had a moderate or good prognosis. Physicians appear to use information not identified in the prognostic factor analysis to reach their conclusions.
|
| [4] |
Prognostic Model for Predicting Overall Survival in Children and Adolescents with Rhabdomyosarcoma [J].URL PMID: 25189734 [本文引用: 1] 摘要
BACKGROUND: The purpose of this study was to develop a prognostic model for the survival of pediatric patients with rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) using parameters that are measured during routine clinical management. METHODS: Demographic and clinical variables were evaluated in 1679 pediatric patients with RMS registered in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program from 1990 to 2010. A multivariate Cox proportional hazards model was developed to predict median, 5-year and 10-year overall survival (OS). The Akaike information criterion technique was used for model selection. A nomogram was constructed using the reduced model after model selection, and was internally validated. RESULTS: Of the total 1679 patients, 543 died. The 5-year OS rate was 64.5% (95% confidence interval (CI), 62.1-67.1%) and the 10-year OS was 61.8% (95%CI, 59.2-64.5%) for the entire cohort. Multivariate analysis identified age at diagnosis, tumor size, histological type, tumor stage, surgery and radiotherapy as significantly associated with survival (p <-0.05). The bootstrap-corrected c-index for the model was 0.74. The calibration curve suggested that the model was well calibrated for all predictions. CONCLUSIONS: This study provided an objective analysis of all currently available data for pediatric RMS from the SEER cancer registry. A nomogram based on parameters that are measured on a routine basis was developed. The nomogram can be used to predict 5- and 10-year OS with reasonable accuracy. This information will be useful for estimating prognosis and in guiding treatment selection.
|
| [5] |
Prognostic Factors and Predictive Model in Patients with Advanced Biliary Tract Adenocarcinoma Receiving First-line Palliative Chemotherapy [J].https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24472 URL PMID: 19536892 [本文引用: 1] 摘要
Abstract Top of page Abstract MATERIALS AND METHODS RESULTS DISCUSSION Conflict of Interest Disclosures References BACKGROUND: Advanced biliary tract adenocarcinoma (BTA) has been a rare but fatal cancer. If unresectable, palliative chemotherapy improved the quality and length of life, but to the authors' knowledge, prognostic factors in such patients have not been well established to date. In the current study, prognostic factors were investigated in patients with advanced BTA receiving first-line palliative chemotherapy. METHODS: Data from 213 patients with advanced BTA who were in prospective phase 2 or retrospective studies from September 2000 through October 2007 were used. RESULTS: With a median follow-up duration of 29.7 months, the median overall survival (OS) was 7.3 months (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 6.3 months-8.3 months). A Cox proportional hazards model indicated that metastatic disease (hazards ratio [HR], 1.521; P = .011), intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma (HR, 1.368; P = .045), liver metastasis (HR, 1.845; P 1.5 but 鈮 2.2; n = 75), and 3.6 months (95% CI, 2.9 months-4.1 months) for the high-risk group (PI > 2.2; n = 70 [ P < .001]). CONCLUSIONS: Five prognostic factors in patients with advanced BTA were identified. The predictive model based on PI appears to be promising and may be used for the management of individual patients and to guide the design of future clinical trials, although external validation is needed. Cancer 2009. 2009 American Cancer Society.
|
| [6] |
Nomogram of Naive Bayesian Model for Recurrence Prediction of Breast Cancer [J].https://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2016.22.2.89 URL [本文引用: 1] 摘要
Abstract Objectives: Breast cancer has a high rate of recurrence, resulting in the need for aggressive treatment and close follow-up. However, previously established classification guidelines, based on expert panels or regression models, are controversial. Prediction models based on machine learning show excellent performance, but they are not widely used because they cannot explain their decisions and cannot be presented on paper in the way that knowledge is customarily represented in the clinical world. The principal objective of this study was to develop a nomogram based on a na茂ve Bayesian model for the prediction of breast cancer recurrence within 5 years after breast cancer surgery. Methods: The nomogram can provide a visual explanation of the predicted probabilities on a sheet of paper. We used a data set from a Korean tertiary teaching hospital of 679 patients who had undergone breast cancer surgery between 1994 and 2002. Seven prognostic factors were selected as independent variables for the model. Results: The accuracy was 80%, and the area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC) of the model was 0.81. Conclusions: The nomogram can be easily used in daily practice to aid physicians and patients in making appropriate treatment decisions after breast cancer surgery.
|
| [7] |
Development of Novel Breast Cancer Recurrence Prediction Model Using Support Vector Machine [J].https://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2012.15.2.230 Magsci [本文引用: 1] 摘要
Purpose: The prediction of breast cancer recurrence is a crucial factor for successful treatment and follow-up planning. The principal objective of this study was to construct a novel prognostic model based on support vector machine (SVM) for the prediction of breast cancer recurrence within 5 years after breast cancer surgery in the Korean population, and to compare the predictive performance of the model with the previously established models. Methods: Data on 679 patients, who underwent breast cancer surgery between 1994 and 2002, were collected retrospectively from a Korean tertiary teaching hospital. The following variables were selected as independent variables for the prognostic model, by using the established medical knowledge and univariate analysis: histological grade, tumor size, number of metastatic lymph node, estrogen receptor, lymphovascular invasion, local invasion of tumor, and number of tumors. Three prediction algorithms, with each using SVM, artificial neural network and Cox-proportional hazard regression model, were constructed and compared with one another. The resultant and most effective model based on SVM was compared with previously established prognostic models, which included Adjuvant! Online, Nottingham prognostic index (NPI), and St. Gallen guidelines. Results: The SVM-based prediction model, named 'breast cancer recurrence prediction based on SVM (BCRSVM),' proposed herein outperformed other prognostic models (area under the curve = 0.85, 0.71, 0.70, respectively for the BCRSVM, Adjuvant! Online, and NPI). The BCRSVM evidenced substantially high sensitivity (0.89), specificity (0.73), positive predictive values (0.75), and negative predictive values (0.89). Conclusion: As the selected prognostic factors can be easily obtained in clinical practice, the proposed model might prove useful in the prediction of breast cancer recurrence. The prediction model is freely available in the website (http://ami.ajou.ac.kr/bcr/).
|
| [8] |
乳腺癌患者预后模型的研究 [D].Study on the Prognosis Model for Breast Cancer [D]. |
| [9] |
Risk Classification of Cancer Survival Using ANN with Gene Expression Data from Multiple Laboratories [J].https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2014.02.006 URL Magsci [本文引用: 1] 摘要
Numerous cancer studies have combined gene expression experiments and clinical survival data to predict the prognosis of patients of specific gene types. However, most results of these studies were data dependent and were not suitable for other data sets. This study performed cross-laboratory validations for the cancer patient data from 4 hospitals. We investigated the feasibility of survival risk predictions using high-throughput gene expression data and clinical data. We analyzed multiple data sets for prognostic applications in lung cancer diagnosis. After building tens of thousands of various ANN architectures using the training data, five survival-time correlated genes were identified from 4 microarray gene expression data sets by examining the correlation between gene signatures and patient survival time. The experimental results showed that gene expression data can be used for valid predictions of cancer patient survival classification with an overall accuracy of 83.0% based on survival time trusted data. The results show the prediction model yielded excellent predictions given that patients in the high-risk group obtained a lower median overall survival compared with low-risk patients (log-rank test P-value < 0.00001). This study provides a foundation for further clinical studies and research into other types of cancer. We hope these findings will improve the prognostic methods of cancer patients. (C) 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
|
| [10] |
三种数据挖掘算法在电子病历知识发现中的比较 [J].
【目的】从异构的电子病历数据中发现疾病危险因素,为数据挖掘与知识发现提供借鉴。【方法】选取集各种结构为一身的临床电子病历数据,利用决策树、逻辑回归和神经网络三种数据挖掘算法分别建立疾病危险因素预测模型,对三种预测模型进行比较分析和统计学评价。【结果】决策树预测模型在查准率、召回率上高于逻辑回归和神经网络,在总体性能上决策树最优,但三者差别不大。【局限】未对电子病历属性进行优化选择。【结论】决策树在危险因素的发现与疾病的预测方面优于逻辑回归和神经网络。研究中建立基于数据挖掘算法的异构数据源知识发现框架,为今后领域知识发现和知识库构建以及数据挖掘算法的选择提供一定借鉴和参考。
Discovering Knowledge from Electronic Medical Records with Three Data Mining Algorithms [J].
【目的】从异构的电子病历数据中发现疾病危险因素,为数据挖掘与知识发现提供借鉴。【方法】选取集各种结构为一身的临床电子病历数据,利用决策树、逻辑回归和神经网络三种数据挖掘算法分别建立疾病危险因素预测模型,对三种预测模型进行比较分析和统计学评价。【结果】决策树预测模型在查准率、召回率上高于逻辑回归和神经网络,在总体性能上决策树最优,但三者差别不大。【局限】未对电子病历属性进行优化选择。【结论】决策树在危险因素的发现与疾病的预测方面优于逻辑回归和神经网络。研究中建立基于数据挖掘算法的异构数据源知识发现框架,为今后领域知识发现和知识库构建以及数据挖掘算法的选择提供一定借鉴和参考。
|
| [11] |
A Coupling Approach of a Predictor and a Descriptor for Breast Cancer Prognosis [J].https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8794-7-S1-S4 URL PMID: 4101306 [本文引用: 1] 摘要
In cancer prognosis research, diverse machine learning models have applied to the problems of cancer susceptibility (risk assessment), cancer recurrence (redevelopment of cancer after resolution), and
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2016 [R/OL]. [ |
| [14] |
Principled Computational Methods for the Validation and Discovery of Genetic Regulatory Networks [D]. |
| [15] |
Prediction of Different Types of Liver Diseases Using Rule Based Classification Model [J]. |
| [16] |
A Bayesian Network Approach for Modeling Local Failure in Lung Cancer [J].https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/56/6/008 URL PMID: 21335651 [本文引用: 1] 摘要
Locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients suffer from a high local failure rate following radiotherapy. Despite many efforts to develop new dose-volume models for early detection of tumor local failure, there was no reported significant improvement in their application prospectively. Based on recent studies of biomarker proteins' role in hypoxia and inflammation in predicting tumor response to radiotherapy, we hypothesize that combining physical and biological factors with a suitable framework could improve the overall prediction. To test this hypothesis, we propose a graphical Bayesian network framework for predicting local failure in lung cancer. The proposed approach was tested using two different datasets of locally advanced NSCLC patients treated with radiotherapy. The first dataset was collected retrospectively, which comprises clinical and dosimetric variables only. The second dataset was collected prospectively in which in addition to clinical and dosimetric information, blood was drawn from the patients at various time points to extract candidate biomarkers as well. Our preliminary results show that the proposed method can be used as an efficient method to develop predictive models of local failure in these patients and to interpret relationships among the different variables in the models. We also demonstrate the potential use of heterogeneous physical and biological variables to improve the model prediction. With the first dataset, we achieved better performance compared with competing Bayesian-based classifiers. With the second dataset, the combined model had a slightly higher performance compared to individual physical and biological models, with the biological variables making the largest contribution. Our preliminary results highlight the potential of the proposed integrated approach for predicting post-radiotherapy local failure in NSCLC patients.
|
| [17] |
基于禁忌搜索算法的贝叶斯网络在疾病预测与诊断中的应用 [D].The Application of Bayesian Network Based on Tabu Search Algorithm in Diseases Prediction and Diagnosis [D]. |
| [18] |
A Biogeography-Based Optimization Algorithm Hybridized with Tabu Search for the Quadratic Assignment Problem [J].URL PMID: 26819585 [本文引用: 1] 摘要
Abstract The quadratic assignment problem (QAP) is an NP-hard combinatorial optimization problem with a wide variety of applications. Biogeography-based optimization (BBO), a relatively new optimization technique based on the biogeography concept, uses the idea of migration strategy of species to derive algorithm for solving optimization problems. It has been shown that BBO provides performance on a par with other optimization methods. A classical BBO algorithm employs the mutation operator as its diversification strategy. However, this process will often ruin the quality of solutions in QAP. In this paper, we propose a hybrid technique to overcome the weakness of classical BBO algorithm to solve QAP, by replacing the mutation operator with a tabu search procedure. Our experiments using the benchmark instances from QAPLIB show that the proposed hybrid method is able to find good solutions for them within reasonable computational times. Out of 61 benchmark instances tested, the proposed method is able to obtain the best known solutions for 57 of them.
|
| [19] |
Probabilistic Modeling of Short Survivability in Patients with Brain Metastasis from Lung Cancer [J].https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.02.005 URL PMID: 25804445 [本文引用: 1] 摘要
The prediction of substantially short survivability in patients is extremely risky. In this study, we proposed a probabilistic model using Bayesian network (BN) to predict the short survivability of patients with brain metastasis from lung cancer. A nationwide cancer patient database from 1996 to 2010 in Taiwan was used. The cohort consisted of 438 patients with brain metastasis from lung cancer. We utilized synthetic minority over-sampling technique (SMOTE) to solve the imbalanced property embedded in the problem. The proposed BN was compared with three competitive models, namely, naive Bayes (NB), logistic regression (LR), and support vector machine (SVM). Statistical analysis showed that performances of BN, LR, NB, and SVM were statistically the same in terms of all indices with low sensitivity when these models were applied on an imbalanced data set. Results also showed that SMOTE can improve the performance of the four models in terms of sensitivity, while keeping high accuracy and specificity. Further, the proposed BN is more effective as compared with NB, LR, and SVM from two perspectives: the transparency and ability to show the relation of factors affecting brain metastasis from lung cancer; it allows decision makers to find the probability despite incomplete evidence and information; and the sensitivity of the proposed BN is the highest among all standard machine learning methods.
|
| [20] |
禁忌搜索算法的贝叶斯网络模型在冠心病影响因素分析中的应用 [J].https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.06.031 URL [本文引用: 1] 摘要
以10 792例冠心病调查数据为例,依据禁忌搜索算法构建冠心病患病及其影响因素的贝叶斯网络模型,用极大似然估计法计算网络各节点的条件概率,并分析冠心病的影响因素,评价贝叶斯网络模型相对于传统的logistic回归模型在疾病影响因素分析中的优劣,探讨贝叶斯网络模型在临床研究中的适用性.分析结果表明,贝叶斯网络可以揭示冠心病各影响因素间的关联及与冠心病的关系,比logistic回归分析更符合实际理论,表明贝叶斯网络模型在冠心病影响因素分析中具有较好的适用性及应用前景.
Using the Tabu-search-algorithm-based Bayesian Network to Analyze the Risk Factors of Coronary Heart Diseases [J].https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.06.031 URL [本文引用: 1] 摘要
以10 792例冠心病调查数据为例,依据禁忌搜索算法构建冠心病患病及其影响因素的贝叶斯网络模型,用极大似然估计法计算网络各节点的条件概率,并分析冠心病的影响因素,评价贝叶斯网络模型相对于传统的logistic回归模型在疾病影响因素分析中的优劣,探讨贝叶斯网络模型在临床研究中的适用性.分析结果表明,贝叶斯网络可以揭示冠心病各影响因素间的关联及与冠心病的关系,比logistic回归分析更符合实际理论,表明贝叶斯网络模型在冠心病影响因素分析中具有较好的适用性及应用前景.
|
| [21] |
肿瘤登记数据库的临床应用 [J].https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-5144.2013.04.016 URL [本文引用: 1] 摘要
随着肿瘤发病率及死亡率的急剧上升,其研究已成为医学研究的焦点,肿瘤数据资料具有数据量大、无序、检索不方便的特点,这就对资料的搜集与统计分析提出了更高要求,肿瘤登记数据库应运而生,它作为循证医学发展的产物,适用于对大量无序的肿瘤相关数据进行组织管理和快速的查询检索。着重介绍SEER数据库,总结国内外肿瘤登记数据库的临床应用情况及存在问题。
Clinical Applications of the Tumor Registry Database [J].https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-5144.2013.04.016 URL [本文引用: 1] 摘要
随着肿瘤发病率及死亡率的急剧上升,其研究已成为医学研究的焦点,肿瘤数据资料具有数据量大、无序、检索不方便的特点,这就对资料的搜集与统计分析提出了更高要求,肿瘤登记数据库应运而生,它作为循证医学发展的产物,适用于对大量无序的肿瘤相关数据进行组织管理和快速的查询检索。着重介绍SEER数据库,总结国内外肿瘤登记数据库的临床应用情况及存在问题。
|

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |